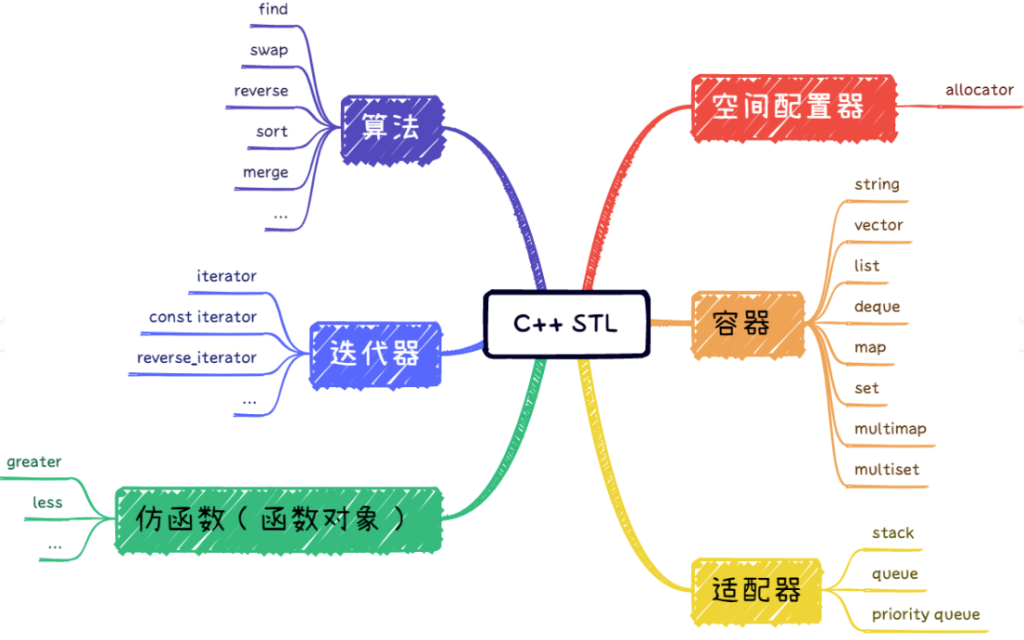
一、常用容器(数据结构)
- 序列容器
vector (动态数组)
#include <vector>
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3};
v.push_back(4); // 末尾添加元素
v.pop_back(); // 删除末尾元素
v.size(); // 元素数量
v[0]; // 访问元素(不检查边界)
v.at(0); // 访问元素(检查边界)
v.insert(v.begin()+1, 5); // 在指定位置插入
v.erase(v.begin()+1); // 删除指定位置元素deque (双端队列)
#include <deque>
deque<int> d = {1, 2, 3};
d.push_front(0); // 头部插入
d.push_back(4); // 尾部插入
d.pop_front(); // 头部删除
d.pop_back(); // 尾部删除list (双向链表)
#include <list>
list<int> l = {1, 2, 3};
l.push_front(0); // 头部插入
l.push_back(4); // 尾部插入
l.pop_front(); // 头部删除
l.pop_back(); // 尾部删除
l.insert(++l.begin(), 5); // 在第二个位置插入
l.erase(--l.end()); // 删除最后一个元素- 关联容器
set (有序集合)
#include <set>
set<int> s = {3, 1, 2};
s.insert(4); // 插入元素
s.erase(2); // 删除元素
s.count(3); // 检查是否存在(返回0或1)
s.find(3); // 返回迭代器,找不到返回s.end()map (有序键值对)
#include <map>
map<string, int> m = {{"Alice", 25}, {"Bob", 30}};
m["Charlie"] = 28; // 插入或修改
m.erase("Bob"); // 删除
m.count("Alice"); // 检查键是否存在
m.find("Alice"); // 返回迭代器
for(auto& p : m) {
cout << p.first << ": " << p.second << endl;
}unordered_set/unordered_map (哈希表实现)
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
unordered_set<int> us = {3, 1, 2};
unordered_map<string, int> um = {{"Alice", 25}, {"Bob", 30}};
// 接口与set/map类似,但无序- 容器适配器
stack (栈)
#include <stack>
stack<int> s;
s.push(1); // 压栈
s.pop(); // 弹栈(不返回元素)
s.top(); // 访问栈顶
s.empty(); // 是否为空queue (队列)
#include <queue>
queue<int> q;
q.push(1); // 入队
q.pop(); // 出队(不返回元素)
q.front(); // 访问队首
q.back(); // 访问队尾priority_queue (优先队列)
#include <queue>
priority_queue<int> pq; // 默认大顶堆
pq.push(3); // 插入元素
pq.push(1);
pq.push(4);
pq.top(); // 访问最大元素(4)
pq.pop(); // 删除最大元素
// 小顶堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> min_pq;
// 自定义
auto cmp = [](int a, int b) { return a > b; }; // 小顶堆比较函数
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
二、常用算法
- 排序和搜索
#include <algorithm>
vector<int> v = {3, 1, 4, 2};
// 排序
sort(v.begin(), v.end()); // 升序
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>()); // 降序
// 二分查找(要求已排序)
binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 3); // 返回bool
auto it = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 2); // 第一个不小于2的元素
auto it = upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 2); // 第一个大于2的元素- 查找算法
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3, 2, 4};
// 线性查找
auto it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3); // 返回迭代器
// 计数
int cnt = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 2); // 返回2
// 条件计数
cnt = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int x){return x%2==0;}); // 偶数个数- 修改序列算法
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4};
// 反转
reverse(v.begin(), v.end()); // v变为{4, 3, 2, 1}
// 填充
fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 0); // 全部填充为0
// 去重(要求已排序)
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
auto last = unique(v.begin(), v.end()); // 返回去重后的新结尾
v.erase(last, v.end()); // 删除重复元素
// 复制
vector<int> v2(v.size());
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin());- 数值算法
#include <numeric>
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4};
// 累加
int sum = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0); // 10
// 内积
vector<int> v2 = {2, 3, 4, 5};
int product = inner_product(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), 0); // 1 * 2 + 2 * 3 + 3 * 4 + 4 * 5 = 40
// 部分和
vector<int> partial(v.size());
partial_sum(v.begin(), v.end(), partial.begin()); // {1, 3, 6, 10}- 其他实用算法
// 遍历处理
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int& x){ x *= 2; });
// 变换
vector<int> result(v.size());
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), result.begin(), [](int x){return x*x;});
// 生成序列
vector<int> nums(5);
iota(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 10); // {10, 11, 12, 13, 14}
// 随机洗牌
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());
// 最大/最小值
auto min_it = min_element(v.begin(), v.end());
auto max_it = max_element(v.begin(), v.end());三、迭代器
vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 正向迭代器
for(auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
// 反向迭代器
for(auto rit = v.rbegin(); rit != v.rend(); ++rit) {
cout << *rit << " ";
}
// 常量迭代器
for(auto cit = v.cbegin(); cit != v.cend(); ++cit) {
// *cit = 10; // 错误,不能修改
}四、函数对象和Lambda表达式
// 函数对象
struct Greater {
bool operator()(int a, int b) const {
return a > b;
}
};
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater());
// Lambda表达式
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int a, int b) {
return a > b;
});
// 带捕获的Lambda
int threshold = 3;
auto count = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), [threshold](int x) {
return x > threshold;
});五、实用技巧
- 使用auto简化代码:
for(auto& x : v) { x *= 2; }- 使用emplace代替insert/push (避免不必要的拷贝):
vector<pair<int, string>> v;
v.emplace_back(1, "one"); // 直接在容器中构造- 移动语义提高效率:
vector<string> v;
string s = "data";
v.push_back(move(s)); // 移动而非拷贝- 结构化绑定(C++17):
map<string, int> m = {{"Alice", 25}, {"Bob", 30}};
for(const auto& [name, age] : m) {
cout << name << ": " << age << endl;
}- 使用make_shared/make_unique (智能指针):
auto ptr = make_shared<int>(42);
auto uptr = make_unique<vector<int>>(10, 1);
