CGO 是 Go 语言中一项强大的功能,它允许 Go 程序直接调用 C 和 C++ 的代码。本文将全面介绍 CGO 的核心概念、最佳实践以及常见问题的解决方案,并通过一个完整的 Dijkstra 算法实现案例展示其实际应用。
1. CGO 基础入门
1.1 基本语法结构
在 Go 文件中使用 CGO 的基本格式如下:
/*
// C 或 C++ 代码
#include <stdio.h>
*/
import "C"
func main() {
C.puts(C.CString("Hello from CGO!"))
}
关键点:
- 注释块中的代码由 CGO 处理
import "C"必须紧跟在注释块后- 通过
C.前缀访问 C 函数和类型
1.2 类型系统映射
Go 与 C 的类型对应关系:
| Go 类型 | C 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
C.char | char | 字符类型 |
C.int | int | 整型 |
C.float | float | 单精度浮点 |
*C.char | char* | C 字符串 |
unsafe.Pointer | void* | 通用指针 |
2. 高级集成技术
2.1 调用 C++ 代码
要调用 C++ 代码,需要特别注意名称修饰和异常处理:
// mylib.h
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
void cppFunction();
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
/*
#cgo CXXFLAGS: -std=c++11
#cgo LDFLAGS: -L. -lmylib
#include "mylib.h"
*/
import "C"
func main() {
C.cppFunction()
}
2.2 内存管理最佳实践
跨语言内存管理原则:
- 谁分配谁释放
- 使用 defer 确保资源释放
- 避免跨语言传递复杂对象
/*
#include <stdlib.h>
*/
import "C"
import "unsafe"
func main() {
cstr := C.CString("Hello")
defer C.free(unsafe.Pointer(cstr)) // 确保释放
C.puts(cstr)
}
3. 实战案例:Dijkstra 算法(单源最短路)集成
3.1 C++ 实现
dijkstra.h:
#ifndef DIJKSTRA_H
#define DIJKSTRA_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
typedef struct {
int* path;
int length;
int total_cost;
} PathResult;
void free_path_result(PathResult* result);
PathResult* dijkstra(int graph[], int vertices, int start, int end);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
dijkstra.cpp:
#include "dijkstra.h"
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 优先队列节点
struct Node {
int vertex;
int distance;
bool operator<(const Node& other) const {
return distance > other.distance; // 最小堆
}
};
PathResult* dijkstra(int graph[], int vertices, int start, int end) {
// 初始化距离和前驱节点
vector<int> dist(vertices, INT_MAX);
vector<int> prev(vertices, -1);
vector<bool> visited(vertices, false);
// 使用邻接矩阵 (假设graph是vertices×vertices的一维数组)
auto get_weight = [&](int u, int v) {
return graph[u * vertices + v];
};
// 优先队列
priority_queue<Node> pq;
pq.push({start, 0});
dist[start] = 0;
// Dijkstra算法核心
while (!pq.empty()) {
Node current = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (visited[current.vertex]) continue;
visited[current.vertex] = true;
for (int v = 0; v < vertices; ++v) {
int weight = get_weight(current.vertex, v);
if (weight > 0) { // 有边存在
int new_dist = dist[current.vertex] + weight;
if (new_dist < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = new_dist;
prev[v] = current.vertex;
pq.push({v, new_dist});
}
}
}
}
// 构建返回结果
PathResult* result = new PathResult();
result->total_cost = dist[end];
// 回溯路径
vector<int> path;
for (int at = end; at != -1; at = prev[at]) {
path.push_back(at);
}
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
// 转换为C数组
result->length = path.size();
result->path = new int[path.size()];
copy(path.begin(), path.end(), result->path);
return result;
}
void free_path_result(PathResult* result) {
if (result) {
delete[] result->path;
delete result;
}
}
3.2 Go 调用代码
package main
/*
#cgo CXXFLAGS: -std=c++11
#cgo LDFLAGS: -L. -ldijkstra
#include "dijkstra.h"
*/
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
// 示例图 (邻接矩阵)
graph := []int32{ // 使用 int32 确保与 C.int 大小一致
0, 10, 0, 30, 100,
0, 0, 50, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 10,
0, 0, 20, 0, 60,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
}
// 转换为 C 兼容类型
cGraph := (*C.int)(unsafe.Pointer(&graph[0]))
vertices := C.int(5)
start := C.int(0)
end := C.int(4)
// 调用 Dijkstra
result := C.dijkstra(cGraph, vertices, start, end)
defer C.free_path_result(result)
// 处理结果
path := (*[1 << 30]C.int)(unsafe.Pointer(result.path))[:result.length:result.length]
goPath := make([]int, result.length)
for i := range goPath {
goPath[i] = int(path[i])
}
fmt.Printf("Shortest path from %d to %d:\n", start, end)
fmt.Println("Path:", goPath)
fmt.Println("Total cost:", result.total_cost)
}
4. 跨平台编译指南
4.1 Windows 系统
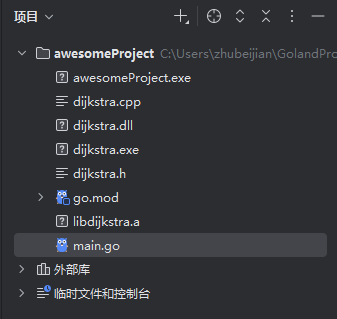
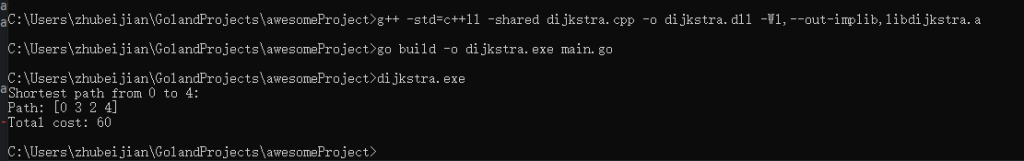
# 编译 DLL
g++ -std=c++11 -shared dijkstra.cpp -o dijkstra.dll -Wl,--out-implib,libdijkstra.a
# 编译 Go
set CGO_CXXFLAGS=-std=c++11
go build
4.2 Linux/macOS 系统
# 编译 SO
g++ -std=c++11 -fPIC -shared dijkstra.cpp -o libdijkstra.so
# 编译 Go
CGO_CXXFLAGS="-std=c++11" go build
5. 性能优化技巧
- 减少跨语言调用:批量处理数据
- 内存池技术:重用已分配内存
- 并行处理:结合 Go 的 goroutine
/*
static inline int fastAdd(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
*/
import "C"
func batchAdd(a, b []int32) []int32 {
result := make([]int32, len(a))
for i := range a {
result[i] = int32(C.fastAdd(C.int(a[i]), C.int(b[i])))
}
return result
}
6. 常见问题解决方案
问题1:类型转换错误
错误信息:cannot convert &graph[0] (value of type *int) to type *_Ctype_int
解决方案:
// 使用 int32 确保平台一致性
graph := []int32{...}
cGraph := (*C.int)(unsafe.Pointer(&graph[0]))
问题2:C++ 标准库缺失
错误信息:fatal error: vector: No such file or directory
解决方案:
/*
#cgo CXXFLAGS: -std=c++11
*/
问题3:链接错误
错误信息:undefined reference to 'dijkstra'
解决方案:
- 检查函数是否正确定义为
extern "C" - 确保编译时链接了正确的库文件
- 验证函数签名是否一致
7. 安全注意事项
- 指针安全:使用
unsafe.Pointer时要特别小心 - 边界检查:确保数组访问不越界
- 错误处理:检查 C 函数返回值
/*
#include <errno.h>
*/
import "C"
import "syscall"
func safeCall() error {
if C.some_function() == -1 {
return syscall.Errno(C.errno)
}
return nil
}
结语
CGO 为 Go 程序提供了强大的扩展能力,使其能够利用现有的 C/C++ 生态。