逆序对计数示例(基于树状数组)
逆序对(Inversion)是指数组中前面的元素大于后面的元素的对数,即若 i < j 且 a[i] > a[j],则 (a[i], a[j]) 是一个逆序对。树状数组可以高效统计逆序对数量,步骤如下:
算法步骤
- 离散化(可选):
- 若元素值范围很大(如
1e9),需先将数组离散化为1..n的排名,保持大小关系不变。
- 若元素值范围很大(如
- 从右向左遍历:
- 对每个元素
a[i],查询树状数组中 小于a[i]的元素数量(即已处理元素中比a[i]小的数的个数)。 - 逆序对数量 +=
i - query(a[i])(当前元素右侧比它小的数的个数)。 - 将
a[i]插入树状数组(update(a[i], 1))。
- 对每个元素
C++ 实现
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class FenwickTree {
private:
vector<int> tree;
int lowbit(int x) { return x & -x; }
public:
FenwickTree(int n) : tree(n + 1, 0) {}
void update(int x, int delta) {
while (x < tree.size()) {
tree[x] += delta;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int query(int x) {
int res = 0;
while (x > 0) {
res += tree[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
};
int countInversions(vector<int>& nums) {
// 离散化(将原数组映射到1..n的排名)
vector<int> sorted = nums;
sort(sorted.begin(), sorted.end());
sorted.erase(unique(sorted.begin(), sorted.end()), sorted.end());
// 离散化后的数组
for (int& num : nums) {
num = lower_bound(sorted.begin(), sorted.end(), num) - sorted.begin() + 1;
}
FenwickTree ft(nums.size());
int res = 0;
// 从右向左遍历
for (int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
res += ft.query(nums[i] - 1); // 统计比nums[i]小的数的个数
ft.update(nums[i], 1); // 插入当前数
}
return res;
}
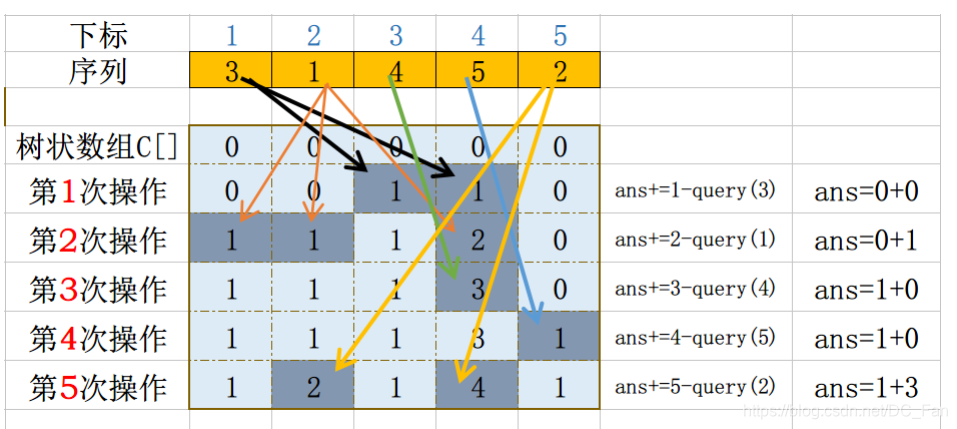
示例分析
输入数组:[3, 1, 4, 2]
- 离散化后:
[2, 1, 3, 4](原值3的排名为2,1的排名为1,依此类推)。 - 从右向左处理:
-
i=3(值4):query(3-1)=0,逆序对+=0,插入4。 -
i=2(值2):query(2-1)=1(1比2小),逆序对+=1,插入2。 -
i=1(值1):query(1-1)=0,逆序对+=0,插入1。 -
i=0(值3):query(2-1)=1(1比3小),逆序对+=1,插入3。
-
- 总逆序对:
0 + 1 + 0 + 1 = 2(实际逆序对为(3,1)和(4,2))。
时间复杂度
• 离散化:O(nlogn)(排序 + 去重)。
• 树状数组操作:O(nlogn)(每次 update 和 query 为 O(logn))。
• 总复杂度:O(nlogn),优于暴力 O(n2)。
关键点
• 离散化:必须将原始值压缩到连续整数,否则树状数组空间爆炸。
• 从右向左遍历:确保每次查询时,树状数组中只包含当前元素右侧的数。
• 逆序对计算:query(a[i]-1) 统计的是 严格小于 a[i] 的数的个数。
扩展问题
- 如果数组中有重复元素:离散化时保留重复值,
query(a[i]-1)仍能正确统计严格小于的数的个数。 - 求数组中每个元素的逆序数:在遍历时记录每个
i的query(a[i]-1),存入结果数组。